About the Course
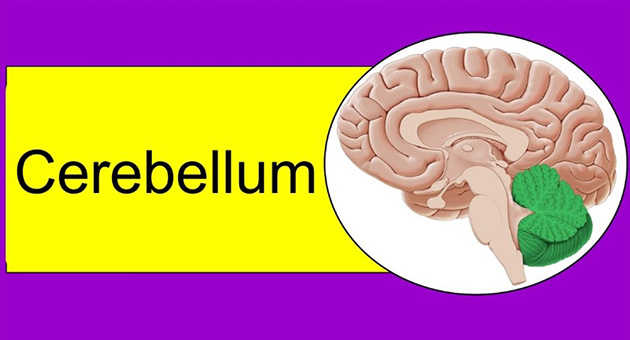
Cerebellum lies in posterior cranial fossa posterior to Pons, Medulla & fourth ventricle. Cerebellum has midline vermis & two cerebellar hemispheres. Cerebellum is divided anatomically, phylogenetically & functionally into lobes by deep fissures. Cerebellum has outer gray matter, inner white matter &. masses of gray matter (nuclei) embedded deeply in substance of white matter. Cerebellum receives afferents from muscle spindles, Golgi tendon organs, spinal cord, brain stem nuclei, visual system, auditory system, vestibular system & cerebral cortex through different tracts. Cerebellum integrates all the information received by it through afferents. This information is used by the cerebellum to smoothly coordinate ongoing movements, modulate muscle tone, participate in motor planning & to maintain balance by influencing descending tracts. Cerebellar lesions result in unsteady gait, abnormalities in eye movements, hypotonia, unstable joints & appendicular ataxia.-
Lesson 1 - External & Internal Features of Cerebellum
Video
Assessment
-
Lesson 2 - Connections of Cerebellum & Cerebellar dysfunctions
Video
Assessment
-
Discussion Forum
Discussion Forum
-
Feedback
Feedback
4.5
Course Rating
2 Reviews
-
50%
-
50%
-
0%
-
0%
-
0%
-
Deepak Kumar
11-09-2024
Good learning content provided on this portal. Good experience to watch video content for better understanding.
-
Piyush Awasthi
11-09-2024
Thanks NMCN for such wonderful learning